What causes facial cyst? Get insights on cyst on face, sebaceous, pictures, cysts that won’t pop, infected, under the skin, causes of the cyst, removal and how to get rid of them.
Cyst on Face Causes
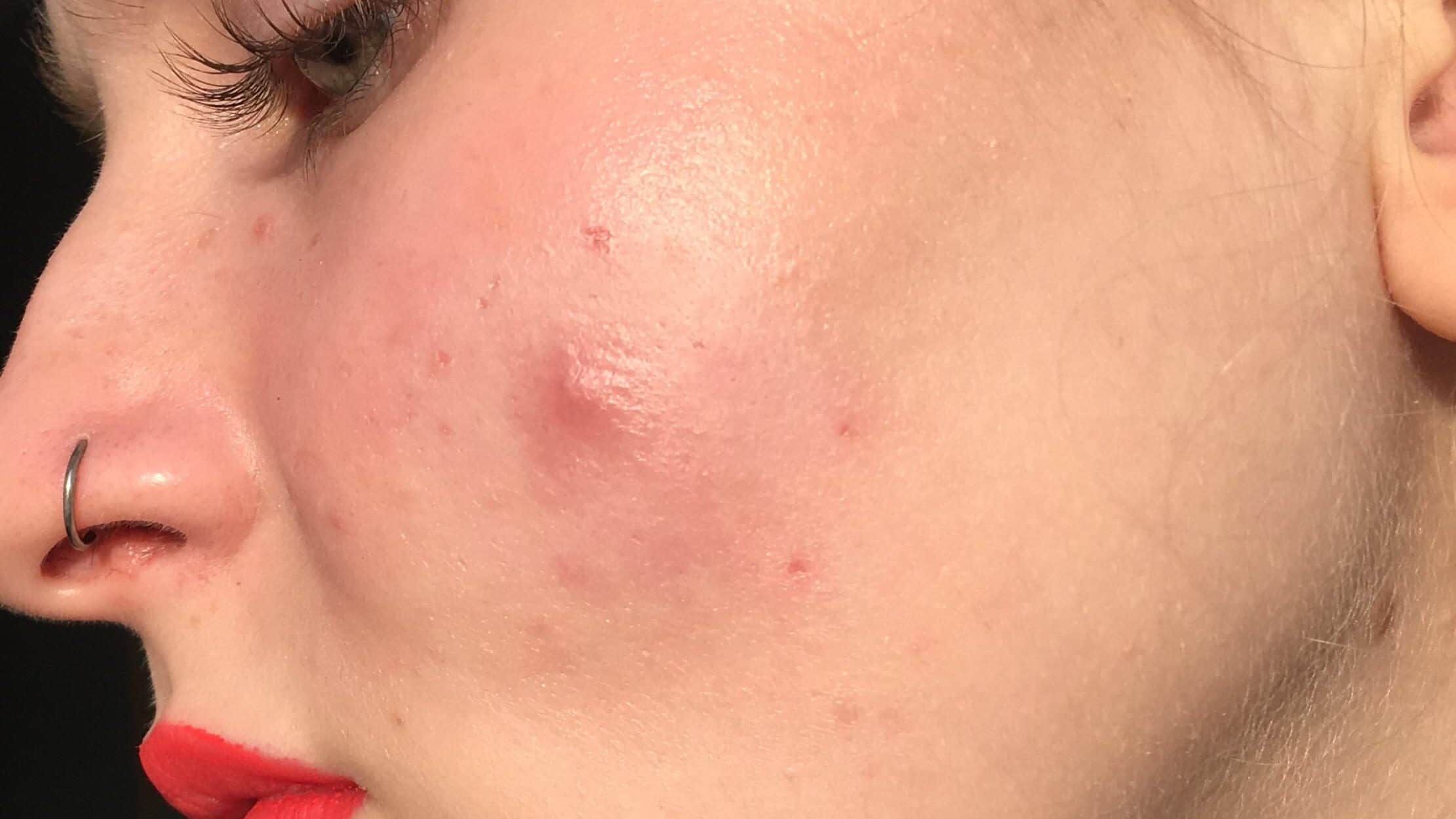
Sebaceous cysts are the most common noncancerous cyst on face. Cysts are the abnormalities in the body that can have liquid or the semiliquid material. Sebaceous cysts are usually mostly found on the face, neck, or even the torso.
A skin cyst is a fluid-filled bump lying just underneath the skin. It’s common and harmless, and may just go away without treatment.
However, it can be hard to say whether the lump is a cyst or something else that will require treatment. So, if you have any sort of lump, it’s best to see your GP so it can be properly diagnosed.
Some people usually confuse cyst on face with the boils or the skin abscesses. Boils and abscesses are very painful collections of the pus that shows an infection. A cyst can go on to become a boil or abscess.
A keratoancanthoma happens when the cells in a hair follicle do not grow as required normally. The growth can be triggered by a minor skin injury in the area that previously had suffered from sun damage. Ultraviolet radiation from the sun exposure is the biggest risk factor in keratoacanthomas.
A keratoacanthoma normally will appear on the sun-damaged skin as a thick growth that contains a central crusted plug. Keratoacanthomas will appear most often in the people who are over the age of 60 and they are normally considered a low-grade skin cancer.
Keratoacanthomas are rapidly increasing, red, dome-shaped bumps that has central craters. Some of the keratoacanthomas might grow to the extremely large sizes, usually 1 to 3 inches in diameter.
Epidermoid cysts, also known as sebaceous cyst on face, are the benign (non-cancerous) skin cysts that are formed by an out pouching from the hair follicle. Most commonly, epidermoid cysts are usually found on the genitals, the chest, and back; but, they also might also happen in other areas of the skin.
In general, epidermoid cysts have a round appearance. A dark portion of the cyst is very visible on the skin. If the cysts have become infected, they will then become red and tender. When the cysts are then squeezed, they might produce a cheesy white discharge.
A cyst on face looks like round, dome-shaped bump. It’s yellow or whitish, often with a small dark plug through which you might be able to squeeze out pus.
It might range in size from a smaller than a pea to a few centimeters across, and grows very slowly.
Skin cysts don’t normally hurt, but might become tender, sore and even red if they become in any way infected. Another sign of infection is foul-smelling pus coming out of it.
Epidermoid cysts are commonly found on the face, neck, shoulders or skin around the genitals.
These cysts affect usually young and middle-aged adults, and are most common in the people who have acne. They don’t usually run in families.
Some cysts form around the hair follicles. These are known as pilar cysts, and it’s typical to find a few of these on the scalp. Unlike epidermoid cysts, pillar cysts strongly run in families. They typically affect middle-aged adults, and women more than men.
A cyst on face that forms on the eyelid is called a chalazion, or meibomian cyst.
Some of the cells in the top layer of the skin produce keratin, a protein that provides skin its strength and flexibility. Normally, the cells move up to the surface of the skin as they begin to die, so they can be shed.
But at times, the cells might move deeper into the skin and then multiply, forming a sac. They secrete keratin into the middle of the sac that forms a thick, yellow paste. This might ooze out of the cyst if it is burst.
Anyone might develop a skin cyst, but an individual is more likely to have one if he has gone through puberty, you have a history of acne or he has injured the skin (if has damaged a hair follicle, for instance).
Skin cyst on face is not in any way contagious.
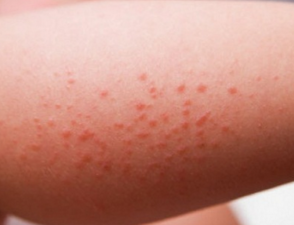
You obtain a pimple when the pore in the skin gets clogged, normally with the dead skin cells. Sometimes the bacteria get much trapped inside the pore, too, leading the area to become red and swollen.
Cystic acne occurs when the infection goes deep into the skin, creating a red, tender bump that’s full of pus. It can hurt or even itch. If the cyst bursts, the infection might spread, leading to more breakouts.
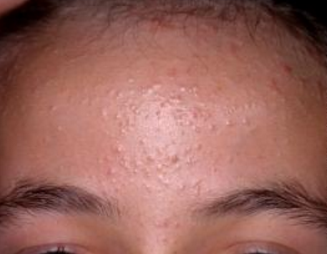
An individual is most likely to develop cystic acne in your teens or even in the early 20s. But it might strike someone as young as 8 or even as old as 50. Your face, upper arms, or shoulders may be affected.
Severe cystic acne is very common in men, but even women get it, too. Women often experience cysts on the lower half of the face.
Folliculitis is the inflammation of the hair follicles. It may be brought about by the infection in the hair follicles, by the chemical irritation or even by physical irritation (for instance, shaving or the friction from clothing). Typical body areas that are involved in folliculitis are the face, thighs, and scalp.
Folliculitis is very common in the people who have diabetes. It also is very common in the people who are obese or have a compromised immune systems.
Sebaceous Cyst on Face
A cyst on face is a sac that is fully filled with a fluid or even a semi-fluid material. Cysts normally develop in various places in the body and can arise from the different tissues in the body. Two of the most common types of cyst that happen under the skin surface are the epidermoid and the pillar cysts. These cysts used to be known as sebaceous cysts but this term is no longer used, as the origin of these cysts is not from the sebaceous glands in the skin.
- An epidermoid cyst is a cyst where the cyst sac forms from cells that usually occur on the top layer of the skin (the epidermis).
- A pillar cyst is a cyst where the cyst sac forms from cells that is similar to those that are in the bottom of hair follicles (where hairs grow from).
In both of the cases, the semi-fluid content of the cyst on face appears a bit like toothpaste. This substance is soggy keratin. Keratin is brought about by skin cells and is the substance that hairs are made from and the substance that covers the top layer of the skin.
Both epidermoid and pillar cysts are the smooth round lumps which you can see and feel just below the skin surface. They are more common. Often they are the small (pea size) but sometimes they slowly get bigger over several months to become a few centimeters in diameter. They appear very similar to each other but can be differentiated from each other if the cells that form the cyst sac are looked at under the microscope.
- Epidermoid cyst on face might affect anyone but are very common in young and the middle-aged adults. They might appear anywhere on the skin but normally develop most commonly on the face, upper back and genitals, eg scrotum.
- Pillar cysts might affect anyone but are very common in middle-aged women. They may appear anywhere on the skin but develop most commonly on the scalp. It is common for the several of them to develop at the same time on the scalp.
Both epidermoid and the pillar cysts normally lead to no symptoms. Occasionally:
- They become much infected, when they can become red, inflamed and even painful. A course of antibiotics will normally clear an infection if it happens.
- The cyst on face can leak the toothpaste-like material on to the skin if the cyst is punctured or damaged.
- A little horn can grow on the skin over the cyst.
- A cyst might form in an uncomfortable place such as in the genital skin or beside a nail.
Infected Sebaceous Cyst
It seems that some of the cells that are usually near to the surface of the skin (cells of the epidermis or the cells in the hair follicles) get much deeper parts of the skin but then continue to multiply. This can occur for several reasons – for instance, following an injury to the skin. The cells that multiply then form into a sac and then produce the keratin that they normally make on the top layer of the skin. The keratin then becomes soggy and thus forms into a toothpaste-like substance.
A tendency to form pillar cysts runs in several families. So, there is a genetic factor in some cases. Epidermoid cysts in themselves are not in any way hereditary and most form for no reason in healthy people. However, some other people who have rare syndromes have several epidermoid cysts as one of their features.
Cyst under Skin
There are several number of the skin conditions that leads to lumps and bumps to appear on the surface or just below the skin. This below list covers some of the very common ones, and includes:
- Skin cysts
- Cherry angioma
- Dermatofibromas
- Epidermoid cysts
- Keratoacanthoma
- Keratosis pilaris
- Neurofibromas
Cyst on face are very noncancerous, closed pockets of the tissue that may be filled up with fluid, pus, or other material.
Cysts are very common on the skin and can appear elsewhere. They feel like the large peas under the surface of the skin. Cysts can develop as a result of infection, clogging of the sebaceous glands (also called the oil glands), or around foreign bodies, such as earrings.
A cherry angioma is a smooth, cherry-red bump on the skin.
Although cherry angiomas normally appear on the trunk of the body, they can happen nearly anywhere. The cause of the cherry angiomas is not established and the growths normally appear on people over the age of about 40.
Cherry angiomas are very small, bright red growths that are very smooth. The size of the growths might vary from the size of a pinhead to about a quarter inch in the diameter.
In most of the cases, cherry angiomas do not need treatment. If they are cosmetically unappealing or are subject to the bleeding, angiomas can be removed by the lasers or electro cautery — the process of burning or destroying tissue by applying a small probe with an electric current that isrunning through it. Removal may lead to scarring.
Dermatofibromas are the harmless round, red-brownish skin growths that are mostly found on the arms and legs. Dermatofibromas have scar tissue and feel like the hard lumps in the skin.
The cause of dermatofibromas is not established either. In most cases, there is no need to treat dermatofibromas. However, the growths may be extracted surgically or may be flattened by being frozen using liquid nitrogen.
Cyst on Head
If the cysts on head do not bother you then it is best just to leave them alone. However, it is worth asking the doctor to check that they are harmless. Sometimes a person who have an epidermoid or pillar cyst requests that it be extracted. This is usually for one of three reasons:
- Cosmetic reasons. For instance, the cyst is in an obvious site like the head and looks much unsightly.
- They are sometimes very easy to catch and traumatize. This usually happens on the scalp when combing hair.
- If the cyst has thus become infected or irritating.
Cyst on Face Won’t Pop
If needed, the cyst on face might usually be easily removed by the simple operation, under the local anesthetic. The surrounding skin is then numbed by injecting some local anesthetic. A small cut (incision) is then made over the cyst.
Cyst on Face Removal or How to Remove
- Try applying a warm compress.Wet a washcloth using warm water. Don’t apply hot water, or it might inflame the skin. Press the washcloth gently against the cyst and the surrounding area. Leave it on until the washcloth becomes cool again to the touch. You might repeat twice if the washcloth cooled down very quickly, and you can do the procedure a few times each day.
- The warm compress can help to disperse the protein or the oil in the cyst and then speed healing; however, it does not work in all the cases.
- Some reports also suggest it may cut the lifespan of the cyst in half.
- Do not try to pop or squeeze the cyst by yourself. Trying to pop or squeeze the cyst will likely only make it worse.
This is due to the fact that cysts can penetrate quite deep into the skin, and if you try to do this procedure on your own (without the help of an experienced physician) you are unlikely to do it effectively.
Instead, you may worsen inflammation and lead to the cyst on face to come back even worse than it was initially due to the incomplete drainage and the inadequate healing. Thus, always see a physician for the procedure rather than trying it on your own.
- Recognize signs of complications.If the cyst has become infected or even inflamed, you will want to see a physician for guidance regarding the treatment. Pay attention and look out for any of the following signs and the symptoms:
- Soreness or even tenderness around the cyst
- Redness that appears around the cyst
- Warmth on the skin that is surrounding the cyst
- Grayish-white fluid leaking from the cyst that is often foul-smelling
- Any of these are an indication that the cyst may be infected or inflamed.
- Move on to medical methods if the cyst doesn’t go away on its own in a month. If you have complications of the cyst, or if it fails to resolve on its own (and more especially if is bothering you in terms of any pain or the cosmetic appearance), do not hesitate to see the doctor. There are several medical options available for the treatment of the facial cysts.
Infected Sebaceous Cyst Treatment
Cysts are normally harmless. If they’re very small and not bothering you, they can just be left alone.
You can find it assists to hold a warm flannel against the skin, to encourage the cyst to heal and even reduce any inflammation.
Don’t try to be tempted to pop the cyst, as if it’s infected, you only risk spreading the infection and if the sac is also left underneath the skin, it can grow back.
Cyst on face usually do not lead to any pain unless they rupture or even become infected or inflamed. Most of the cysts do not disappear on their own without treatment. Some cysts can require to be drained to relieve symptoms.
That involves piercing the cyst with a scalpel and draining it. That doesn’t cure the cyst, however. Some inflamed cysts might be treated with an injection of the cortisone medication to lead to it to shrink. Cyst on face that do not respond to other types of treatments or even reoccur can be extracted surgically if they cause troublesome symptoms.
If you think the cyst is infected, see your doctor as you may require some antibiotics.
If the cyst is bothering you – for instance, it’s catching on the clothes or looks unpleasant – it might be removed. The doctor will use a local anesthetic to numb the skin, make a tiny cut in the skin, and squeeze the cyst out.
The effective treatment of epidermoid cysts need that the sac of the cyst be very much completely removed. If the cyst is then squeezed and the discharge is then forced out without removing the sac, the cyst may return. Usually, a doctor is able to remove the cyst by making only a small incision in the skin. Antibiotics can be prescribed to treat infected cysts.
This procedure will however, leave a scar. Also, the cyst can still grow back at a later date, especially if it was extracted from the scalp or the scrotum (pouch of skin containing the testicles).
Topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics, or even antifungal drugs can be used to treat infections that are associated with folliculitis, depending on the underlying reason. Treatment also involves preventing further damage to the hair follicles. Steps that can assist to achieve this goal are:
- Minimizing the friction from clothing
- Not shaving in the affected area, if possible. If shaving is required, apply a clean new razor blade or an electric razor each time.
- Keeping the area very clean
How to Get Rid of Cyst on Face
Over-the-counter medicines that work on milder cases often have very little effect on the cyst on face. A dermatologist can likely recommend one or more of the following:
- Oral antibiotics help control bacteria and lower inflammation. Sometimes the acne may not respond to antibiotics, although. Or you can find they don’t work as well after a few years.
- Birth-control pills help that some women use in regulating their hormones.
- Prescription-strength creams, or gels with retinoid, a form of vitamin A, may assist unplug the pores and help antibiotics do their job.
- Isotretinoin, formerly also indicated by the trade name known as Accutane, attacks all the causes of acne. You take a pill at least once or even twice daily for about 5 months. For most people, this clears the skin completely and permanently. If it happens again, you may repeat the treatment. Women should avoid becoming pregnant while taking the drug.
- Spironolactone is the medication that assists you get rid of unnecessary water, but also works as a hormone blocker.
Further references;
- Skin cyst: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/skin-cyst/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Cysts, Lumps, Bumps, and Your Skin: http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/guide/cysts-lumps-bumps?page=3
- Epidermoid and Pilar Cysts (Sebaceous Cysts): http://patient.info/health/epidermoid-and-pilar-cysts-sebaceous-cysts-leaflet